ROS is a open-source framework for robot software development. Personally, I think ROS is the future of Robot. In this article, I'll introduce how to work with ROS Navigation Stack from the beginning.
ROS is not a standalone OS, but based on Ubuntu or other Debian distributions. So first we need to install Ubuntu, or other Debian if you like, but it is recommanded to choose Ubuntu for beginners.
At the time of my writing this article, the latest ROS distribution is Kinetic, which ONLY supports Wily (Ubuntu 15.10), Xenial (Ubuntu 16.04) and Jessie (Debian 8) for debian packages. So my choice is Xenial + Kinetic.
The ROS Kinetic Install Guide is very helpful. So I just make a brief summary here.
apt-get install.ros-kinetic-desktop-full if you are using a x86 PC. For ARM, such as Raspberry Pi, you may have to install ROS-base, and then install other individual packages.source /opt/ros/kinetic/setup.bash to your ~/.bashrc. After creating your own workspaces, you have to setup extra environments.There are two ways to create ROS workspace, i.e. catkin and rosbuild. I think catkin is much more easier.
Actually you may follow the ROS beginner tutorials to learn how to create a catkin workspace, and you have to understand ROS packages, nodes, topics, services, parameters, roslaunch, messages, publisher, subscriber and other ROS basics.
Now we are ready to drive the robot with ROS. Before using ROS, I think you should already have a driver program which can send movement command from PC to your robot and receive odometry and other robot state info. And then you need a bridge program to connect ROS with your driver.
My robot is P3DX, the libaria can communicate with robot, controll it and get its state info. And RosAria is the bridge between ROS and libaria.
RosAria subscribes to the cmd_vel topic, so that I can make P3DX run by publishing geometry_msgs/Twist message to it.
And RosAria publishes to the topic pose, sonar, bumper_state, motors_state, etc. I can get info from these topics.
Then I want to display my robot on the RViz and teleop it. The amr-ros-config package contains URDF, .rviz and launch files, with all these stuff, I can display the P3DX model on the RViz and teleop it.
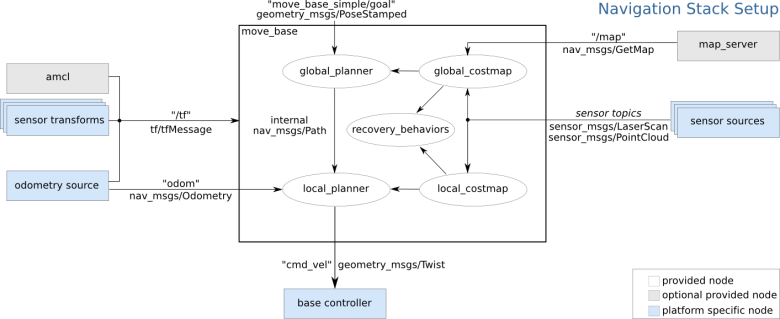
The blue components are what we need to provide. Fortunately, RosAria has done most of the work. odometry source, base controller and sensor sources are all fully provided by RosAria. For sensor transforms, RosAria provides the tf odom->base_link, other sensor frames transform should be provided by us. I didn't use laser, I just used sonar, so I just provided the tf base_link->sonar_frame.
The gray components are optional components that are already implemented. Here I didn't use amcl, I used map_server with a existing map picture. So I need a YAML file to describe map_server parameters.
The white components are required components that are already implemented. What we have to provide is just four configuration files, i.e. costmap_common_params.yaml, global_costmap_params.yaml, local_costmap_params.yaml and base_local_planner_params.yaml.
Finally, a launch file is needed to launch the ROS navigation stack. The launch sequence is like:
OK, now set a goal from RViz, there will be a path and local cosmap, then the robot will go down that path until reaching that goal.